ARGOS is the joint effort of OpenAIRE and EUDAT to deliver an open platform for Data Management Planning that addresses FAIR and Open best practices and assumes no barriers for its use and adoption.
It is an open extensible service - available as a standalone service (OpenDMP) and as a OpenAIRE service (ARGOS) - that simplifies the management, validation, monitoring and maintenance of Data Management Plans. It allows actors (researchers, managers, supervisors etc) to create actionable DMPs that may be freely exchanged among infrastructures for carrying out specific aspects of the Data management process in accordance with the intentions and commitment of Data owners.
ARGOS is a service that is integrated within the OpenAIRE platform and is freely offered for use through the OpenAIRE Service Catalogue and the EOSC Catalogue. ARGOS enhances the OpenAIRE Research Graph while at the same time utilises its underlying services, external sources and semantics to add value to the Dataset Description templates it produces thus increasing validation of DMPs. DMPs in ARGOS are treated as research outputs that can be assigned DOIs, licenses and can be re-distributed in a FAIR manner.
The Name: ARGOS is inspired by Greek mythology, both from Argus Panoptes the hundred-eyed giant and from Argus (Argonaut) builder of Argos ship, for the many-eyes monitoring sense and for the crafting and building for endurance concealing long-term goals.
Research Data Management (RDM) is a vital part of Open Science that lies at the heart of European research for it increases the quality of produced data and ensures integrity and preservation of research outputs. RDM refers to activities undertaken throughout a research lifecycle, spanning from data collection to data process and analysis. Open Access and FAIR principles govern data activities today to foster data discovery, distribution and exploitation, thus accelerating scientific breakthroughs. Coronavirus vaccine is the ultimate example of what can be achieved in a short amount of time when data are openly shared across the global scientific community. RDM urges scientific practices to be adjusted in ways that enable data understandability and re-usability from both humans and machines; services and tools are realised or re-designed to support the shift towards Open and FAIR research outputs.
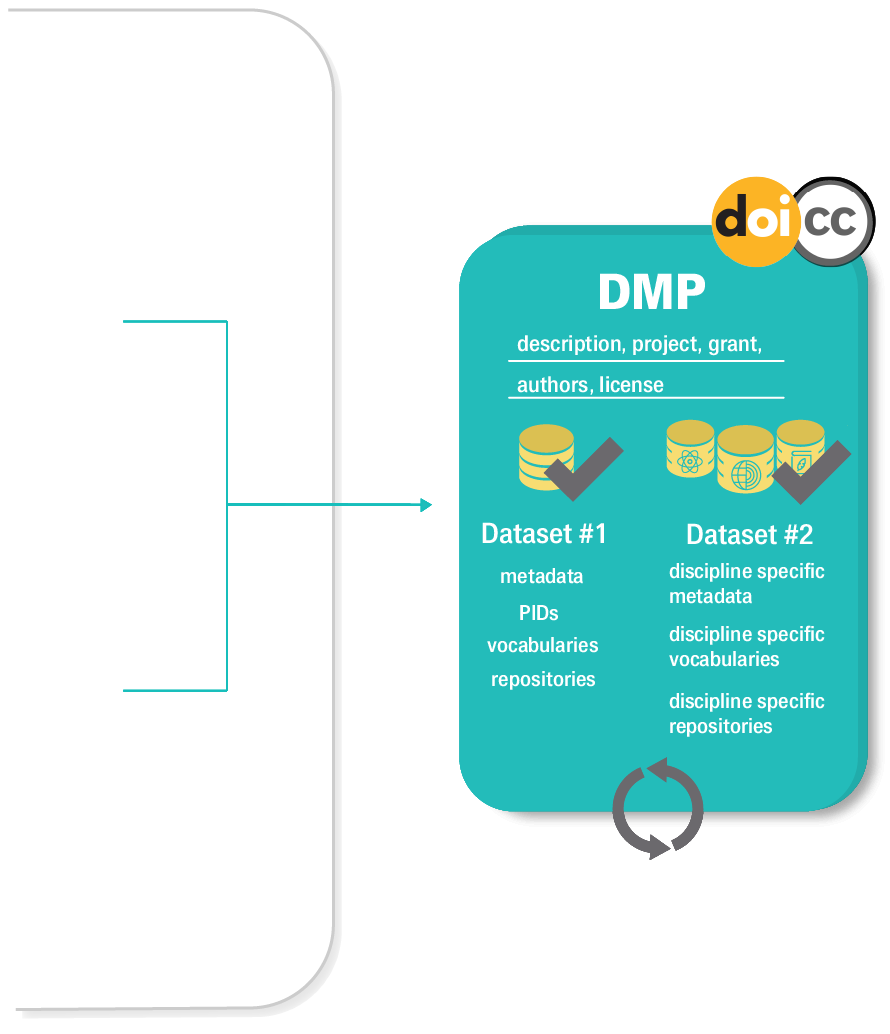
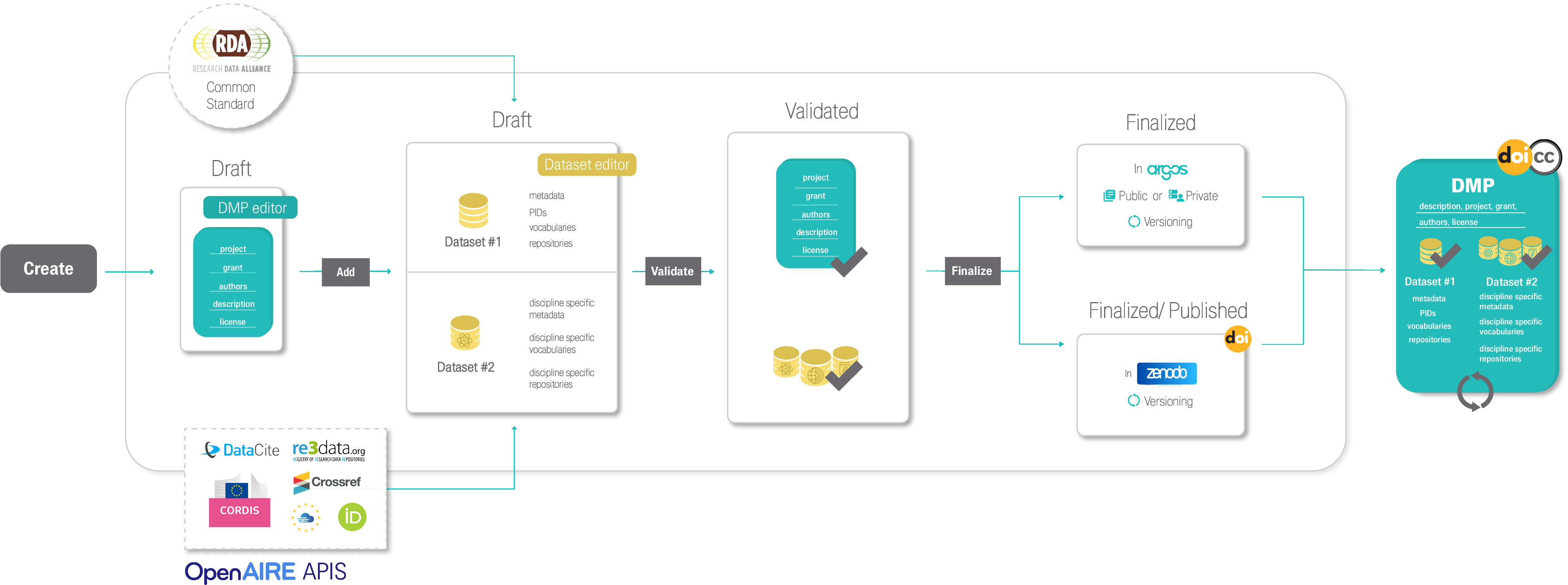
Argos is a service for creating and publishing plans that describe data management activities, commonly known as Data Management Plans (DMPs). The plans are produced as machine-actionable outputs (ma-DMPs), in the form of rich text documents, following Open and FAIR practices and are published in Zenodo. Argos supports RDM at the beginning of research for planning data activities to be performed, as well as throughout and at the end of research for documenting the steps and processes followed according to institutional or funder RDM requirements.
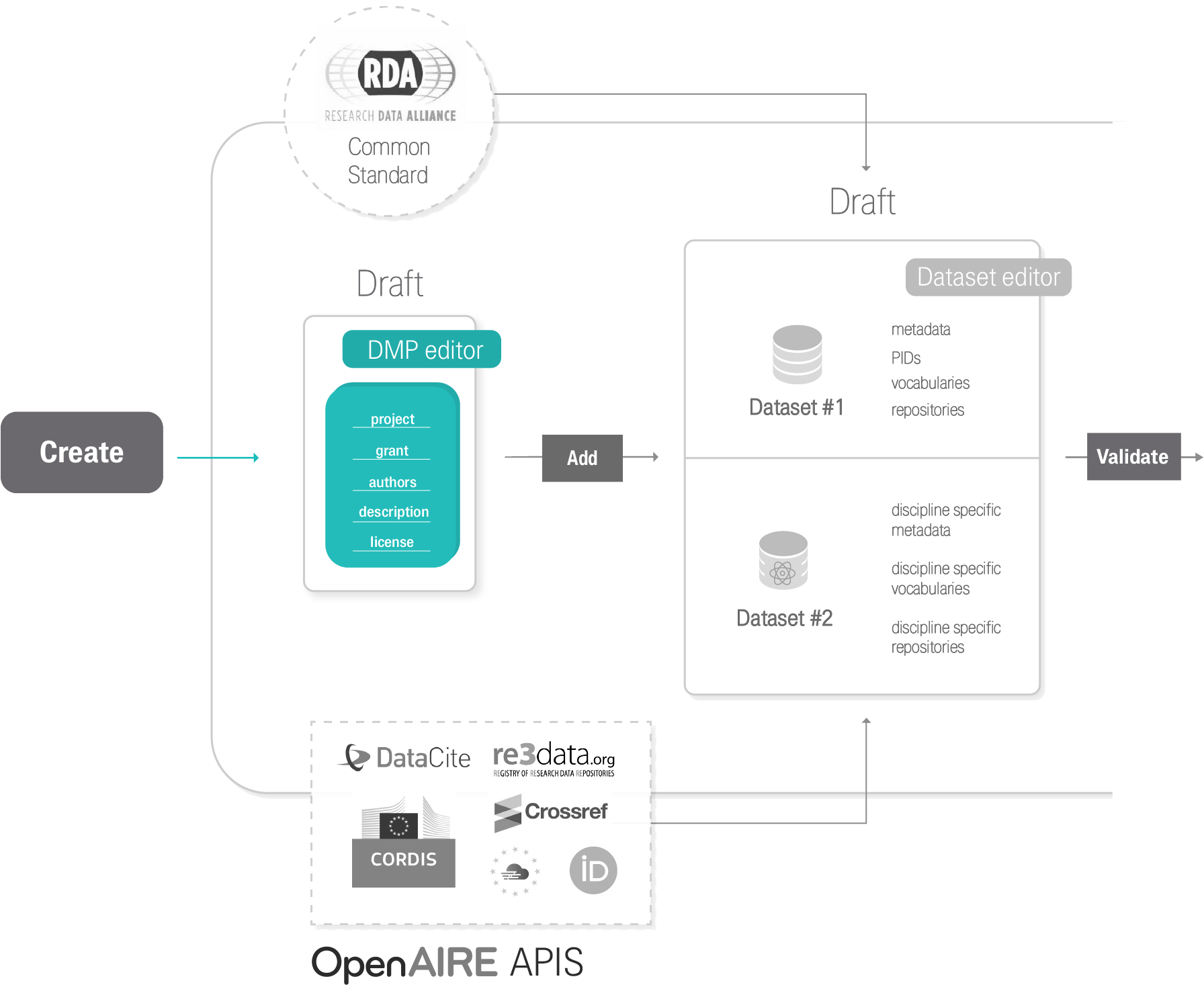
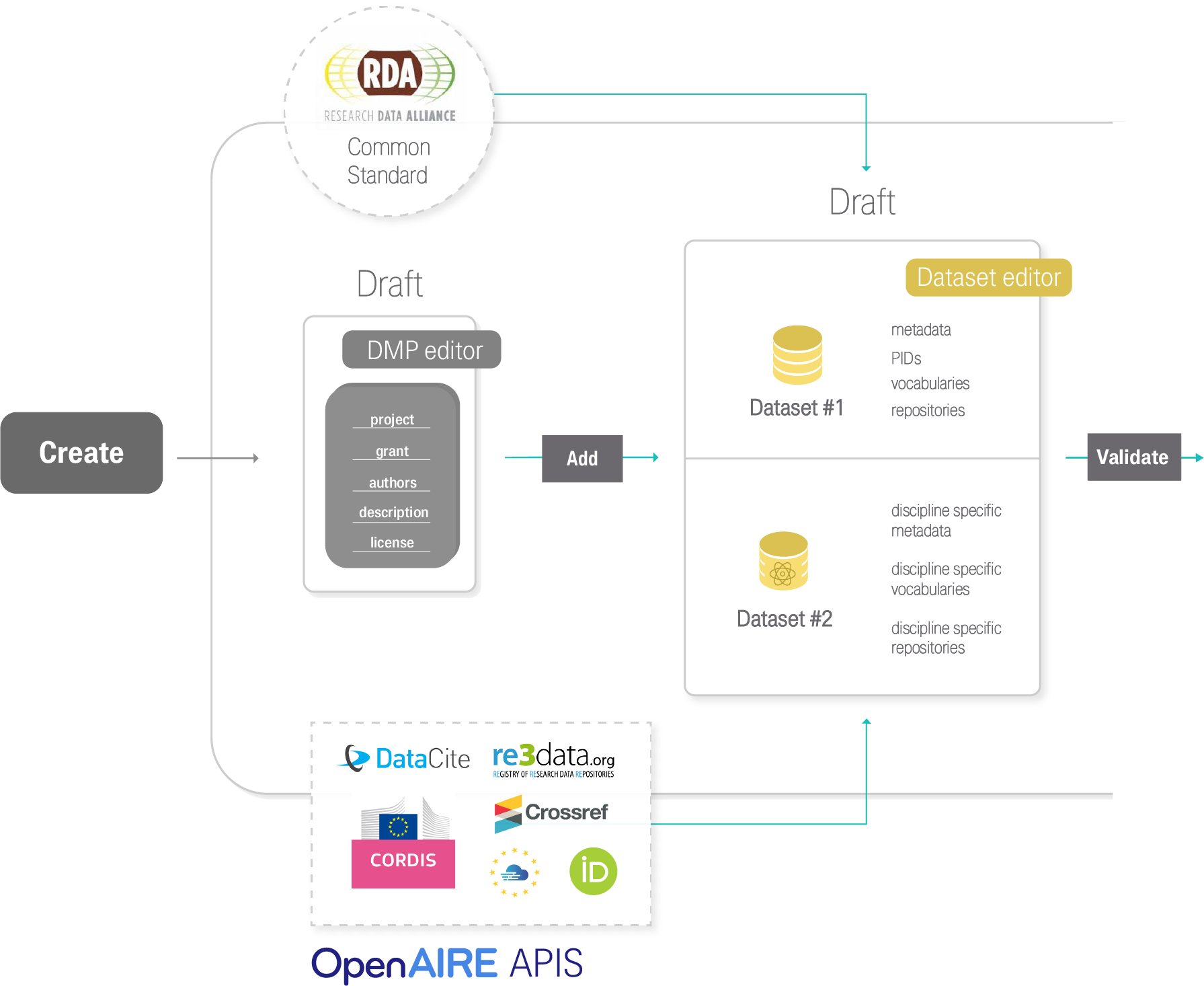
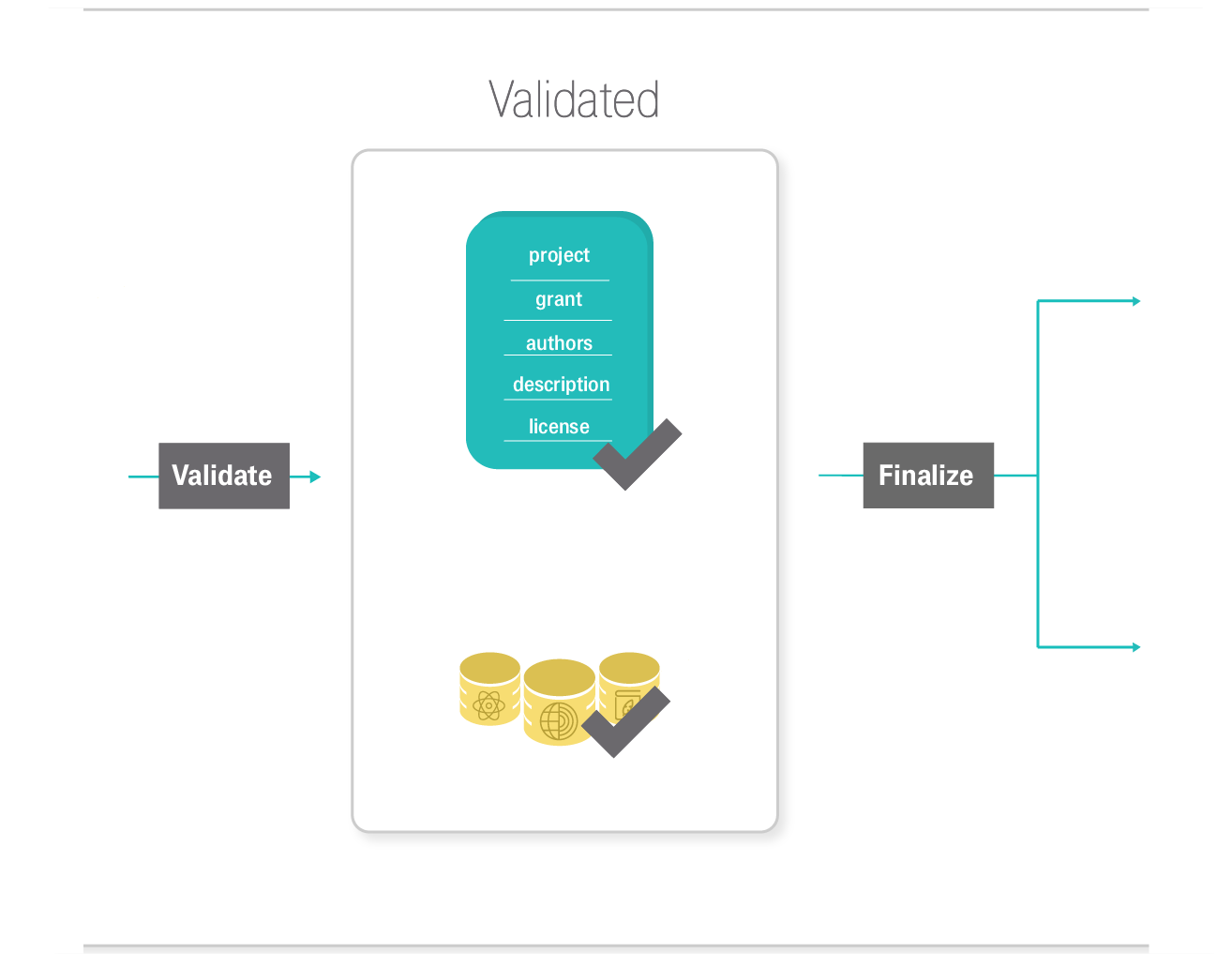
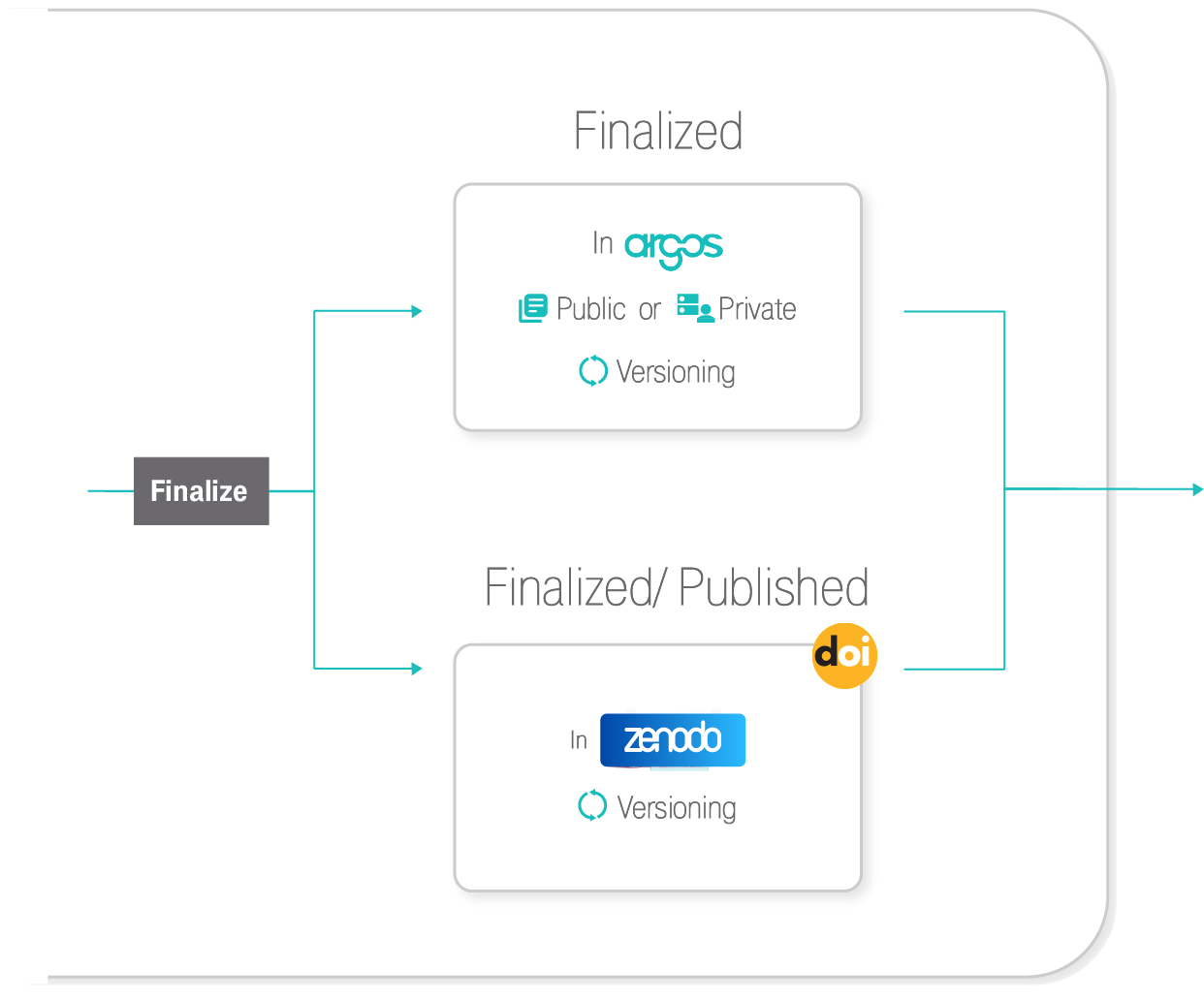
Argos follows a full DMP publication lifecycle. Users create their DMPs and add descriptions for their datasets. DMPs and Datasets are by default created in private mode and can be shared with colleagues to facilitate the writing process. Datasets are added in DMPs per type and / or per scientific discipline that they concern. That way information is well-organized and it is easier to distinguish relevant information from a pool of data activities detailed in a single DMP record. Once created, DMPs and their Datasets are in draft status and are treated as living documents in the Argos environment, meaning that they can be versioned and updated at any time. When ready, users can validate and finalize their DMPs, including corresponding Datasets, and change their visibility status from private to open. Open DMPs in Argos are available and accessible to all from the Public Dashboards. To close the DMP lifecycle, Argos integrates Zenodo, so users are able to publish their DMPs directly from its environment.


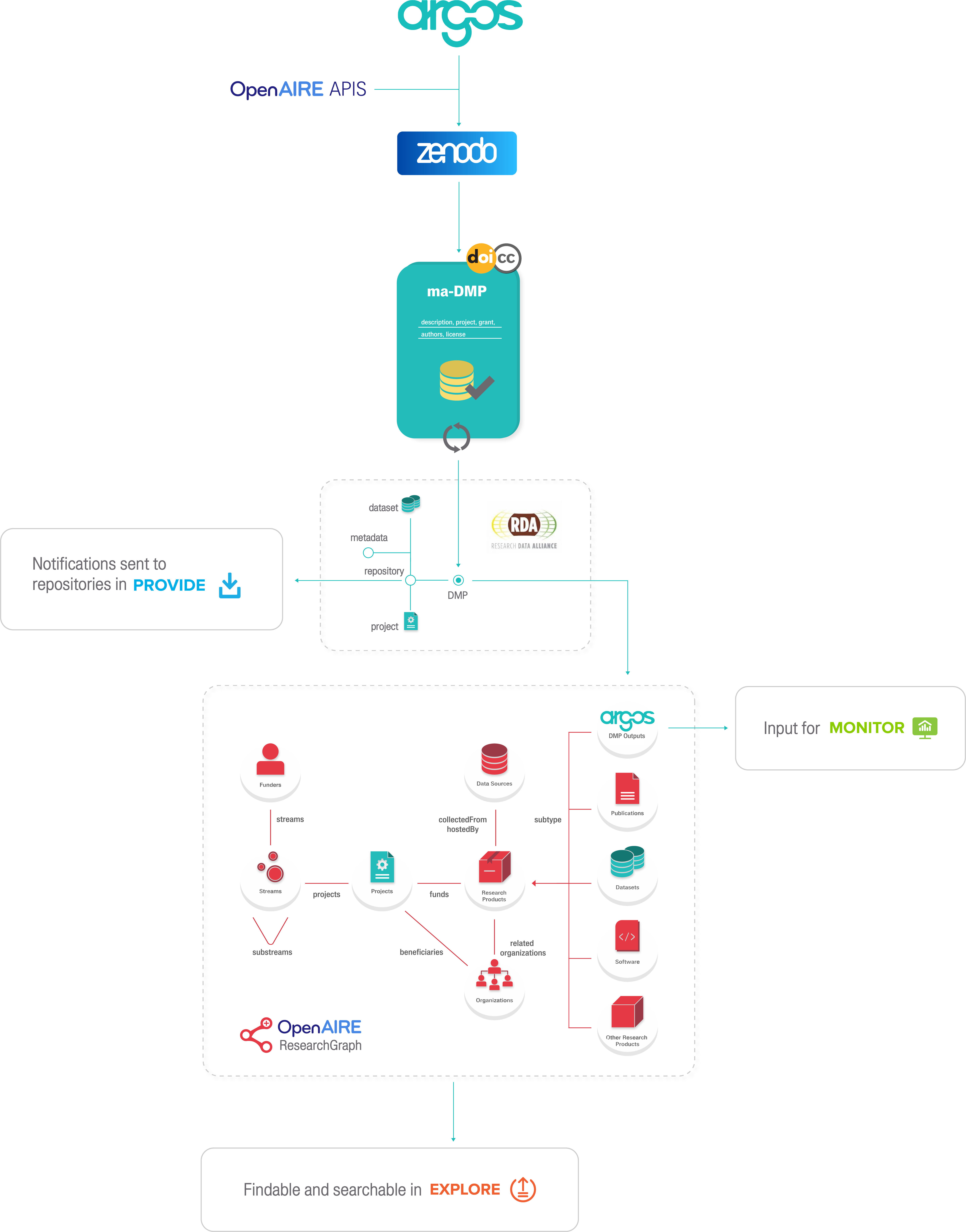
Argos is hooked on the OpenAIRE ecosystem comprising a diverse set of services and tools for Open Science and Scholarly Communication, from technical to educational and consultative in nature. OpenAIRE services and tools are provided for immediate consumption by end-users, i.e. researchers, research communities, research performing or funding organizations and policymakers. Moreover, OpenAIRE services are exploitable by software engineers. Argos integrates other OpenAIRE services to maximise efficiency of operations in Open and FAIR ecosystems and to make connections that add value in Open Science at global scale. OpenAIRE services that Argos connects to are:
Useful Resources
-
Argos RDA output adoption:
https://www.rd-alliance.org/implementing-dmp-common-standard-argos-tool-madmps -
Webinar:
https://www.rd-alliance.org/implementing-dmp-common-standard-argos-tool-madmps (starts at 30:15)
More details on ARGOS as registered in the OpenAIRE services catalogue is available here: http://catalogue.openaire.eu/service/openaire.argos. ARGOS as a Data Management Planning tool within EOSC can be explored in the EOSC catalogue of services here: https://catalogue.eosc-portal.eu/service/openaire.argos
ARGOS is offered as a standalone service, where users can download the source code and co-brand it. Read more on how to implement that in the Resources section.